DeepSeek AI model will stimulate demand for optical communications, optical transceiver modules
DeepSeek's low-cost AI model will stimulate demand for optical communications, and shipments of optical transceiver modules will increase by 56.5% in 2025.

DeepSeek's model reduces the cost of AI training, but the low cost of AI models is expected to expand application scenarios, thereby increasing the number of global data center construction. As a key component of data center interconnection, optical transceiver modules will benefit from the demand for high-speed data transmission. In the future, data transmission between AI servers will require a large number of high-speed optical transceiver modules, which are responsible for converting electrical signals into optical signals and transmitting them through optical fibers, and then converting the received optical signals back into electrical signals. According to statistics from TrendForce, a global market research organization, global shipments of optical transceiver modules above 400Gbps will be 6.4 million in 2023 and about 20.4 million in 2024. It is estimated that by 2025, it will exceed 31.9 million, with an annual growth rate of 56.5%.
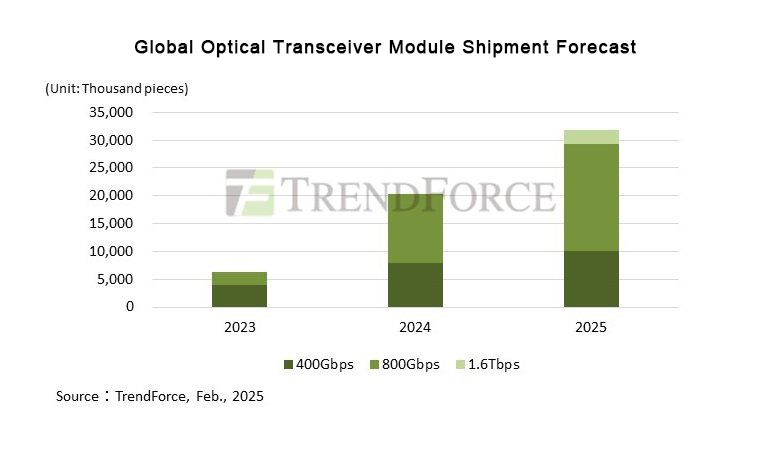
TrendForce pointed out that DeepSeek, CSP and AI software companies will jointly promote the popularization of AI applications, especially in the future, a large amount of data will be generated at the edge, which means that factories, wireless base stations and other places need to build a large number of micro data centers. And through the dense deployment of optical transceiver modules, it is expected that the number of optical communication nodes in each factory will increase by 3-5 times compared with the traditional architecture. Compared with traditional electrical signal transmission, optical fiber communication has higher bandwidth, lower latency and lower signal attenuation, which can meet the stringent requirements of AI servers for high-performance data transmission, making optical communication technology an indispensable key link for AI servers. The demand for AI servers continues to push the growth momentum of optical transceiver modules of 800Gbps and 1.6Tbps. With the upgrade of specifications of traditional servers, the demand for 400Gbps optical transceiver modules has also driven the demand.
Optical transceiver modules are composed of the following key components: laser diode, optical modulator, photo detector, etc. Among them, the laser light source is responsible for generating optical signals, the optical modulator is responsible for modulating electrical signals to optical signals, and the optical sensor is responsible for converting the received optical signals into electrical signals.
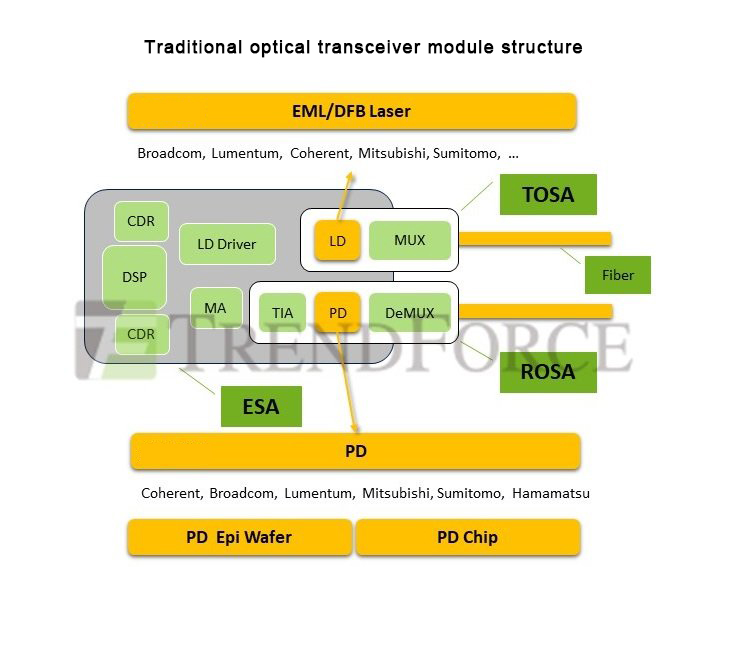
In the laser light source supply chain, since EML lasers have modulation functions, the production technology is difficult. In addition, with the current high-speed transmission demand, a single channel needs to reach an optical transmission speed of 100Gbps, and some specifications even reach 200Gbps, so the entry threshold is relatively high. At present, the main suppliers are mostly concentrated in major companies such as the United States and Japan, such as Broadcom, Coherent, Lumentum and other companies, and rarely outsource.
As for the CW laser (continuous wave laser) in the silicon photonic module, since the optical modulation and wave splitting functions of the laser are integrated by the silicon photonics (SiPh) process, it only needs to provide the light source, and some manufacturers have entered the CW laser foundry supply chain. For example, Lian Ya helps international data center manufacturers to produce CW lasers, and manufacturers such as Huaxing Optoelectronics and Guanghuan combine laser chip processes for foundry.
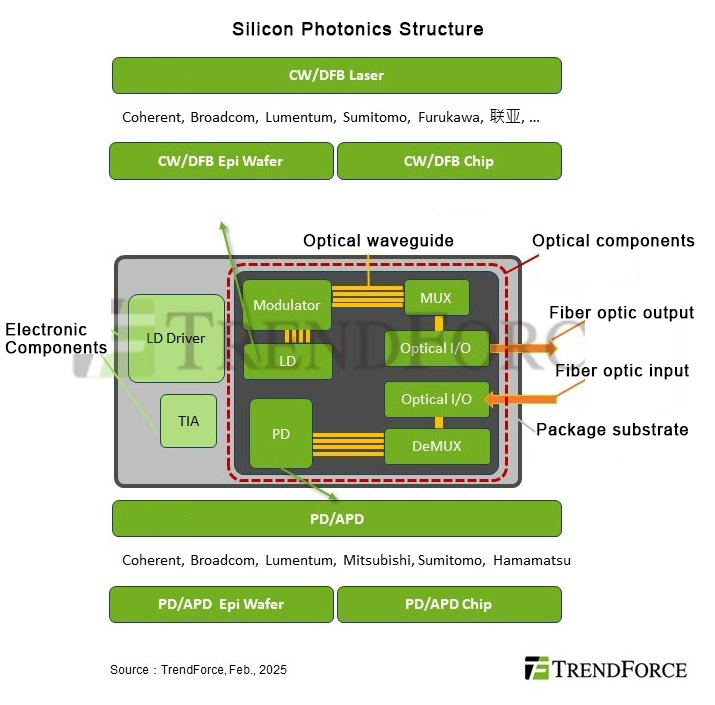
In the optical sensor supply chain, the main suppliers are currently concentrated in the hands of major manufacturers in the United States and Japan that already have laser light sources, such as Broadcom, Coherent, Lumentum, Hamamatsu and other companies. However, as the transmission speed of optical modules increases to around 200Gbps, the challenges of optical sensors are becoming increasingly high. Since the quality of optical sensors depends on the sensitivity of light collection. Therefore, the uniformity of epitaxial material doping or structural defects will affect the light collection effect. At present, in addition to Broadcom's completely self-made 200Gbps Per Lane APD (avalanche photodiode) optical sensors, Coherent's 100Gbps and Lumentum, Hamamatsu and other major manufacturers' 200Gbps APD epitaxy are outsourced to the American company IET.
