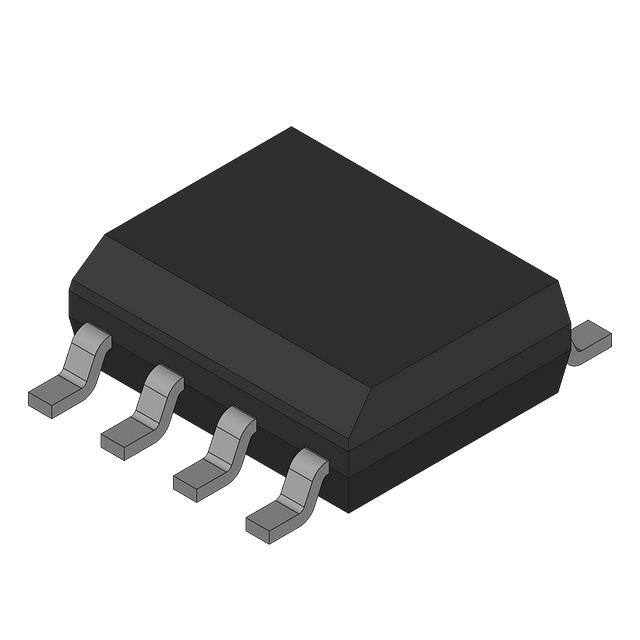
What are the differences between tantalum capacitors and ordinary capacitors
Introduction to tantalum capacitors
Tantalum capacitors (Tantalum Capacitor) are capacitors with tantalum metal as electrode material. Its characteristics are that tantalum metal foil is used as the positive electrode and tantalum oxide film is used as the dielectric, with stable electrical properties and high capacitance. Tantalum capacitors are usually used in circuits with high reliability, high stability and small volume.

Differences between tantalum capacitors and ordinary capacitors
Tantalum capacitors vs Ceramic Capacitors vs Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitors | Ceramic Capacitors | Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode Material | Tantalum metal, with tantalum oxide as dielectric | Ceramic material (usually barium titanate) | Aluminum foil with electrolyte as dielectric |
| Polarity | Polar (must be installed with correct polarity) | Non-polar (can be connected in any direction) | Polar (must be installed with correct polarity) |
| Capacitance Range | Typically 1 µF to 1000 µF | Typically 1 pF to 100 µF | Typically 1 µF to 10000 µF |
| Voltage Range | Typically 4V to 50V | Typically 6V to 100V | Typically 6.3V to 500V |
| Size | Smaller size for higher capacitance values | Very small, especially for low capacitance values | Larger size, especially for high capacitance and voltage |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | Low ESR, suitable for high-frequency applications | Low ESR (for ceramic types) | Higher ESR, not ideal for high-frequency applications |
| Temperature Stability | Excellent temperature stability, wide range (-55°C to +125°C) | Good for most applications, but temperature stability varies by type | Poor temperature stability, can be affected by temperature |
| Leakage Current | Very low leakage current | Very low leakage current | Higher leakage current, especially for larger capacitance |
| Lifespan | Long lifespan, highly reliable | Long lifespan, especially in non-polar applications | Shorter lifespan, especially at higher voltages and temperatures |
| Cost | Higher cost compared to ceramic and aluminum types | Low cost, especially for small values | Moderate to low cost, depending on size and voltage rating |
| Applications | Used in high-reliability applications like military, medical, and aerospace, as well as consumer electronics | Used in general-purpose electronics, filters, decoupling, and high-frequency applications | Used in power supply filtering, audio circuits, DC-DC converters, and larger power applications |
Summary of Key Differences:
Tantalum Capacitors are best for high-reliability applications with smaller sizes and stable performance. They have low ESR and are often used in critical applications.
Ceramic Capacitors are the most common and affordable type, suitable for decoupling, filtering, and general-purpose applications. They are non-polar and offer small sizes with low ESR, but can have temperature-dependent capacitance (especially for certain types like Class II and III).
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors are ideal for high-capacitance needs and are often used in power supply filters, but they have higher ESR and are polar, requiring careful installation.
Each type of capacitor has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice depends on the specific application and requirements.
How Tantalum Capacitors Discharge
Tantalum capacitors discharge similarly to other capacitors, and are discharged in the following ways:
Through a load resistor: If a tantalum capacitor is connected to a load resistor (or other circuit), it will release the stored charge through the load resistor. This is the most common way for capacitors to discharge.
Through a short circuit: If the two ends of a tantalum capacitor are short-circuited (this operation requires caution and may damage the capacitor), the capacitor will discharge rapidly through the short circuit path.
Through circuit design: In some circuits, a discharge path can be designed to use current to flow through the capacitor and release the stored energy.
Precautions during discharge:
1.The discharge rate usually depends on the resistance and capacitance of the load in the circuit.
2.During the discharge process, current may be generated, causing the temperature of the capacitor to rise. Especially when used at high capacitance or high voltage, rapid discharge may cause the capacitor to heat up.
Tantalum capacitors are often used in high-precision circuits due to their high reliability, stability and small size, but due to their high price and polarity requirements, special attention should be paid to the connection polarity when designing. When discharging, tantalum capacitors release the charge through a load resistor or other circuit path. The discharge process should avoid discharging too quickly to avoid damaging the capacitor.
How to identify tantalum capacitors
The method of identifying tantalum capacitors is mainly to distinguish them by their appearance, logo and package type. Here are some common ways to identify tantalum capacitors:
1. Appearance and package type
Tantalum capacitors usually have a specific appearance and package type, which are different from other types of capacitors (such as ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, etc.). Common tantalum capacitor package types include:
Through-hole package:
Cylindrical package: Tantalum capacitors usually have a cylindrical appearance, with an identification point on the top, and usually use different colors of ring marks to indicate polarity (for example, red for positive).
Color: The shell of tantalum capacitors is usually black or brown, and the metal feet are aluminum alloy color.
Surface mount package (SMD):
Small rectangular package: SMD type tantalum capacitors are small in size and usually have rectangular packages (such as CASE B, CASE C, etc.).
Identification: There is usually an identification code or number, such as the **"T"** character for tantalum capacitors. There may not be a clear identification symbol on the package, but sometimes the capacitance value can be seen.
2. Polarity Identification
Tantalum capacitors are polarized capacitors, which means they have positive and negative polarity, and you need to make sure they are connected correctly when connected.
Polarity Identification:
On the shell of lead-lead tantalum capacitors, you will usually see a small black dot or mark, which indicates the negative terminal of the capacitor.
Surface mount tantalum capacitors (SMD) may have a symbol with an arrow pointing to the negative terminal.
Pin Arrangement:
In lead-lead tantalum capacitors, the negative terminal is usually the longer leg (sometimes annotated as "negative"), and the positive leg is shorter.
The polarity identification of surface mount tantalum capacitors is usually distinguished by the arrangement of the pads.
3. Identification and Labeling
The identification of tantalum capacitors usually tells you the value of the capacitor, the operating voltage, the manufacturer and polarity information.
Identification Code:
Many tantalum capacitors will have a number or letter printed on the surface to indicate the value of the capacitor (for example, "6.8 µF" or a similar digital mark). Sometimes the operating voltage and temperature range are also marked.
Capacitance Value and Voltage:
If you see a digital mark, it will usually be in the following format: "3R3" means 3.3 µF; "6.8" means 6.8 µF.
The voltage is usually marked as "6.3V" or "25V", etc. Some models may also be marked with the rated voltage directly.
4. Package and Size
Tantalum capacitors are usually small in size, especially compared to electrolytic capacitors. Common package types of tantalum capacitors are:
A Case: Usually 1.6mm x 0.8mm in size, suitable for surface mounting.
B Case: 3.5mm x 2.8mm in size, also suitable for surface mounting.
C Case: 4.3mm x 4.3mm in size, commonly used for larger capacity tantalum capacitors.
5. Comparison with other capacitor types
Tantalum capacitors have the following characteristics compared to other types of capacitors (such as ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, etc.):
Ceramic capacitors: Ceramic capacitors are usually small, non-polar, and have the capacitance value and operating voltage printed on the surface. The shell is generally round or square. Ceramic capacitors are much larger than tantalum capacitors and have no polarity requirements.
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors: Aluminum electrolytic capacitors have polarity, are usually larger than tantalum capacitors, and are marked with capacitance, voltage, and polarity information on the surface. The shell of aluminum electrolytic capacitors is usually a metal tube.
6. Manufacturer and model of tantalum capacitors
Some well-known tantalum capacitor manufacturers (such as AVX, KEMET, Vishay, Panasonic, etc.) will print the model and manufacturer logo on the surface of tantalum capacitors, which helps to identify the brand and series of tantalum capacitors. Based on the manufacturer and model, you can check the data sheet to confirm the specific parameters of the capacitor.
7. Common Misconceptions
Some surface mount capacitors may look like tantalum capacitors, but they are actually ceramic capacitors or other types of capacitors. In this case, the marking and the material, size, polarity and application environment of the capacitor can help to distinguish.
Tantalum capacitors are mainly identified by the following features:
Package and shape: Tantalum capacitors are usually cylindrical (lead) or small rectangular (SMD package).
Polarity identification: Tantalum capacitors have polarity, usually indicated by shell markings or polarity symbols (such as arrows) to indicate the negative pole.
Marking and capacity: The marked capacitance value, rated voltage and manufacturer information can help identify tantalum capacitors.
Comparison with other capacitor types: Compared with ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors and other types, tantalum capacitors are smaller, more reliable, have good temperature resistance, and have polarity requirements.
Through these methods, you can effectively identify tantalum capacitors and ensure their correct use.